Class & Object
In programming, we have to be able to represent our own data entity. Java allows us to do this by using class and object. We will use java class to represent actual web page under test and utilize them as an object in our test scripts.
In this code note, we will cover following topics:
- Data Type
- Defining a Class
- Creating an Object
› Data Type¶
In Java, working with data values like text is possible thanks to the String data type. A data that you can use in Java has its own data type and its specifications. These data type specification are expressed using Java class and actually utilized by creating an object.
A simple definition of class and object in java:
-
class: It is a blueprint for specifying custom data type. -
object: Ready to use data that was created based on the class.
To give you an analogy, if you want to use iPhone, first someone has to design and represent what an iPhone is. Based on the design, then it can be manufactured and used as an iPhone object. This creation and usage of object based on its specification is called instantiation in programming.
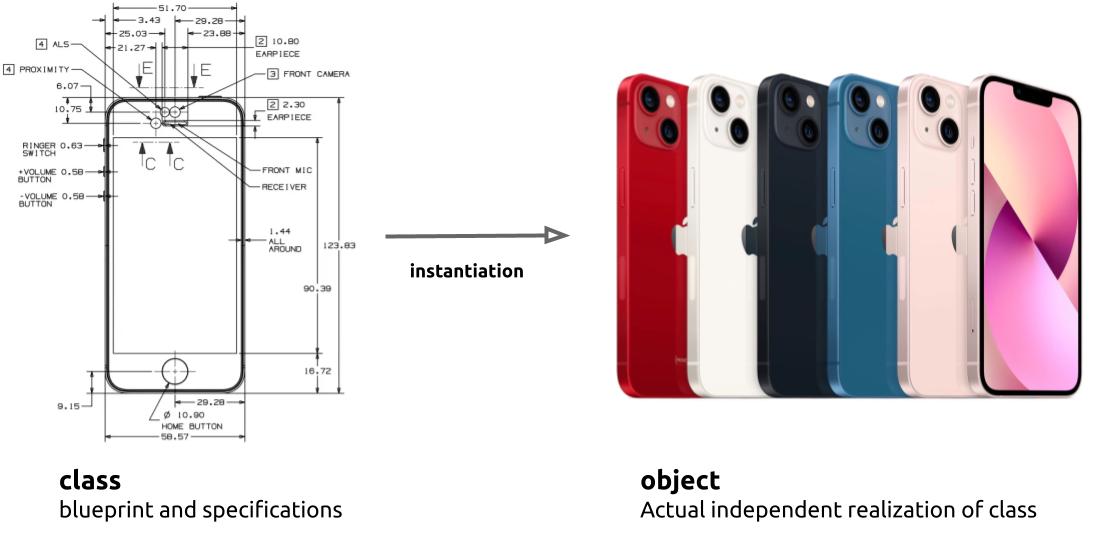
Similarly in java, if you want to represent your own data type first you have to specify it by creating a class. After the specification and designing is done, you can instantiate an object and start using the data type.
So far all the primitive data we have been working with, we were able to work with them because someone has created data type specifications (Class) for each of these data.
| Data Values (Objects) | Data Type | Representation Document (Class) |
|---|---|---|
-10, 0, 23 |
integer numbers | Integer.java |
0.9, 0, -192.23 |
precision numbers | Double.java |
'C', '%', '!' |
characters | Character.java |
true, false |
Logics | Boolean.java |
"Hello", "Good day!" |
Text | String.java |
Without these specifications, Java will not be able to recognize these data value (object).
› Defining a Class¶
Also known as Classification, Java class is a document with .java extension where you describe or specify your custom data type you want Java to recognize. In this document, you provide following 3 sections for the data type you want to create.
- sub-data fields
- operators ( methods )
- usage mechanism ( constructors )
As an example, representing text data in Java involved specifying following 3 sections:

Once these specifications are finalized, it was then expressed in the Java String class file as follows:
String class
This capability of Java where it allows programmer to represent anything they want in their program is the primary reason that it is one of the best programming language in the industry.
› Creating an Object¶
Once the data type specification has been created via Java class. We can use the data type in our Java code as java object. Simply put Java object is working copy of all the code written in the Java class.
Object Creation Syntax:
For example for the String.java class that represents textual data, we can use in our Java program by creating an Object from the class as follows:
Let us see another objects created from following Book.java class.
| Book class | |
|---|---|
We can use this Book class to represent following two books:
