Array
In programming, we need a mechanism to store and manipulate a group of similar data. Java offers a code construct called Array to work with a collection of data as one entity.

In this module, we will cover the following topics to understand an array:
- Intro to Array
- Creating an Array
- Array Indexing
- Array Size
› Intro to Array¶
An array is a collection that holds multiple data values of the same data type. Each data value of the array is called an element.
Array creation syntax:
Array creation example:
Let's see what is going on with the above Example 1 code:
| code segment | explanations |
|---|---|
int[] |
integer array data type specification, The symbol [] specify an array |
ages |
array variable name, name should bea plural |
= |
assignment operator |
new |
keyword that creates new memory space in RAM |
int[4]; |
specifies how many elements should be in the array |
We can also visualize the above array as follows:
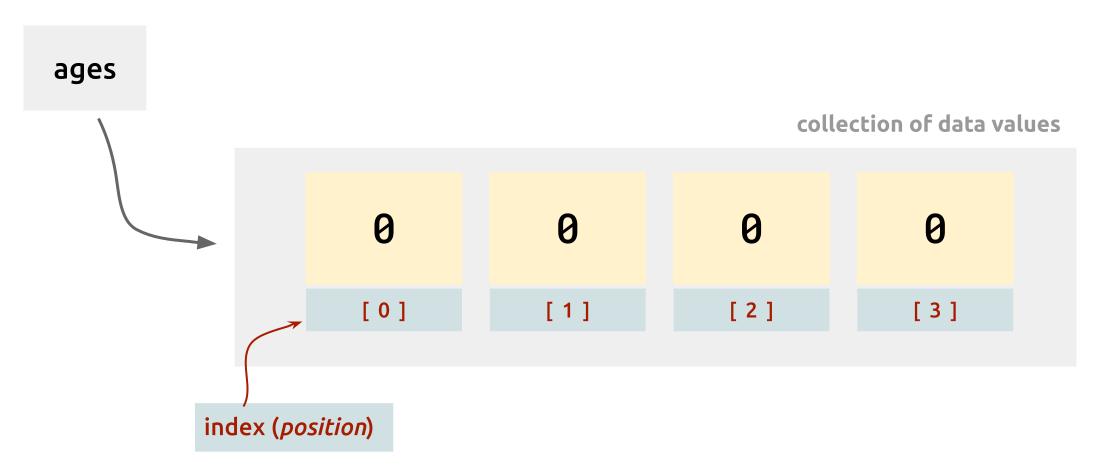
explanation
This integer array is accessible via the ages variable. This array can store four integer data values. This array is currently holds four default integer data values ( 0 ). In order to access or update each of these integer data value, we use the index or position number.
› Creating an Array¶
Arrays can be created using literal syntax or constructor syntax. Both are excellent ways to create an array depending on your needs.
Let's take a look at creating the following ages array on both ways:
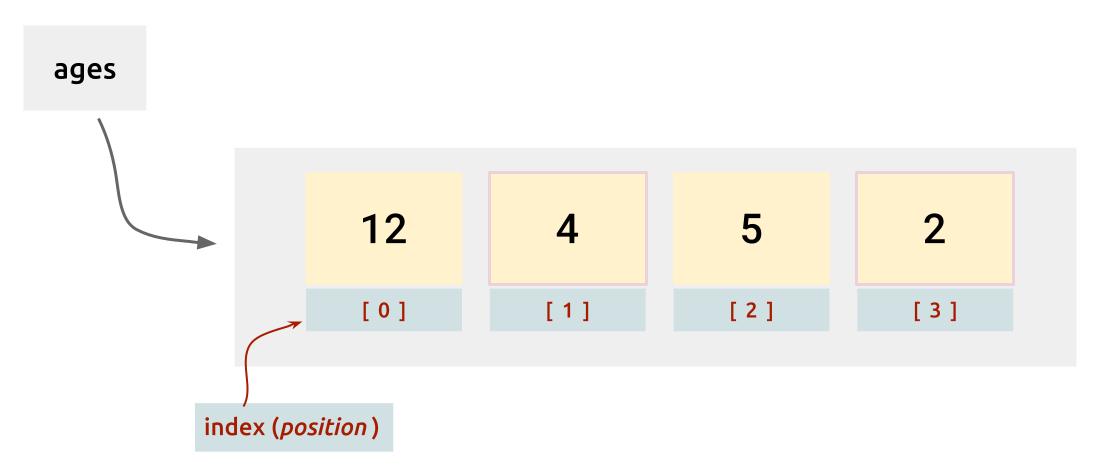
Create an array this way when you know:
- how many elements will be stored in the array.
- data values for each array element.
This way of creating an array has the advantage of creating an array with a specific capacity. For example, we could easily create this
agesarray with 100 elements capacity like this:This is especially helpful when we don't know how many elements we want to group in the array, but we can create large enough to accommodate if we had to group a larger number of age numbers.
Let's see another example of creating same array in two different ways:
| literal syntax | |
|---|---|
J-editor ♞
› Array Indexing¶
An array classifies as an indexed data collection in computer science. This means that each data value in the array can be accessed via index or position number that usually starts with zero. Using this index number to work with one of the data value in the array is generally called indexing.
Indexing syntax:
With indexing, array slot position number starts with the number 0 instead of 1. If the number of elements in ages array is 4, the first element of the array can be accessed via indexing ages[0], and the last element will be ages[3].
Consider indexing example with previous ages array:
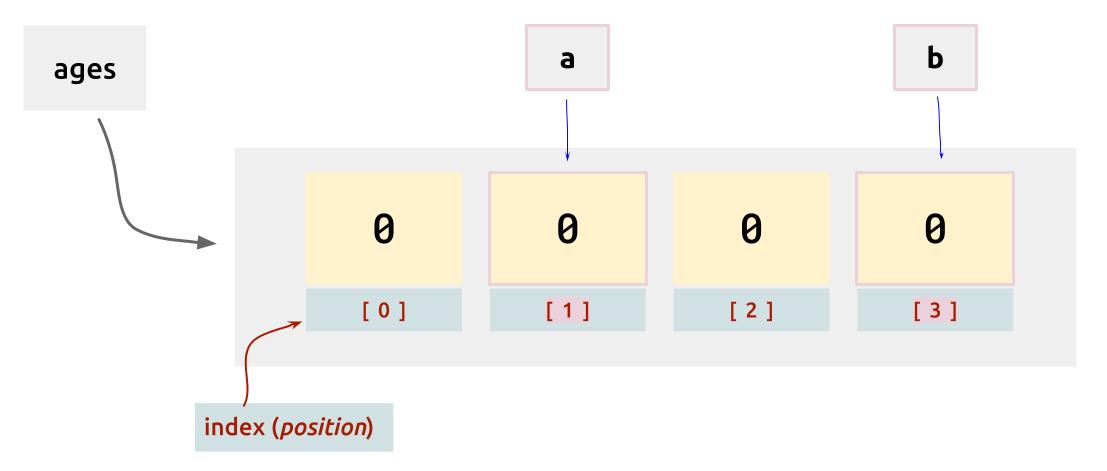
The integer variable a and b will hold the second and fourth element of the ages array. The indexing here for each of these code are as follows:
ages[1]: 2nd slot of an arrayages[3]: 4th slot of an array
It is important to note that if you use a negative integer number for index or a number that is greater than a possible index number, it will result in an exception ( error for programmers ) known as ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Try this indexing sample code in code editor:
J-editor ♞
As you can see, If you do not specify a particular value to each slot of the array, the default value of the data type will be stored instead. For the data types we know so far, their default values are as follows:
| Date Type | Default Data Value |
|---|---|
int |
0 |
double |
0.0 |
char |
empty character symbol |
boolean |
false |
String |
null |
Try the following sample code to see that empty arrays contains data type default values for each of its slots.
J-editor ♞
Assigning data value to array slot:
Assigning or updating the data value for an array slot is also achieved using indexing.
The syntax:
for example if we have an array of integers called age, and if you want to assign 18 as its first element:
Note that assigning incompatible data value to the array, it will result in programming error:
Now, try out this code that creates an integer array, assigns a data value in each of its slots, and display them to the screen one by one.
J-editor ♞
› Array Size¶
Once you declared an array by specifying the number of elements like below:
its size is always fixed, for example, myArray size is always fixed to 5. You CANNOT change the array size. If you need to extend the array size, you need to create a new bigger array with the desired size and copy over the array element values and delete the small array. That is the only way we can increase the array size. However, please note that it is very rated to change the array size in Java programming.
Getting Array Size:
Using .length property of an array will return the size of an array, meaning how many elements are inside of this array.
Also, we can use the .length property of an array to calculate it's last index number.
Let's see an code example:
J-editor ♞