Array Processing Techniques
Storing multiple data in an array is a valuable capability. However, an array's true power lies in processing or manipulating the grouped data. Generally, a programming technique that allows us to work with array elements efficiently is called array processing.

In this code note, we will cover following techniques:
- Introduction
- Populating
- Iterating
- Searching
- Computation
› Introduction¶
We can create a robust program utilizing a loop and array since an array allows element interactions via incremental index numbers. As you can see from following diagram, each element of the array is accessible via its corresponding index number.
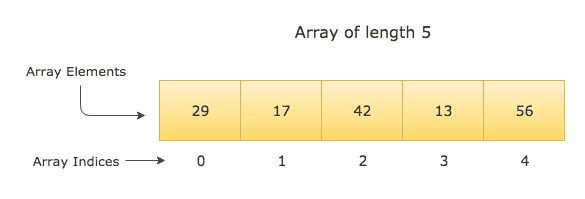
Using loops, we can create matching array indexes for any array. For example, for the array in the above diagram, we can create each of its indexes (0, 1, 2, 3, 4) using for loop:
As such, all array processing techniques in this note utilize loops.
› Populating¶
Populating an array with desired data is one of the most used techniques among test engineers. In our automated test cases, we often need a following collection of random test data.
- random usernames and passwords
- random user ages
- random addresses
- random email address
- random social security numbers
We use these random data for all the registration tests where it's needed for signup-forms.
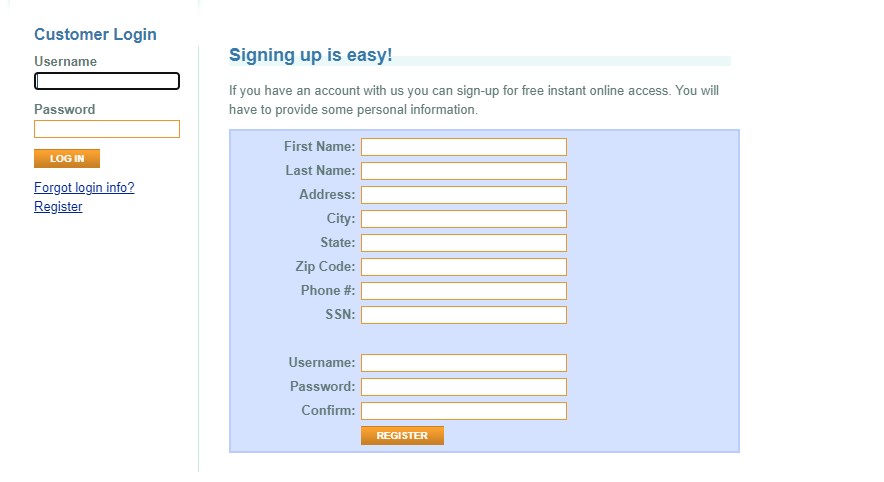
Let's take a look at population an array with few random data we've seen from the list above:
The
usernamesarray now contains 300 fake username. Which we can use in our test cases via index. For example, getting 11th fake username isusernames[10]
The
userAgearray now contains 300 random integer values between0 ~ 100.
› Iterating¶
Visiting each item in the collection is generally called iteration. Array element iteration is basis for all the array processing techniques including searching, manipulating, and retrieving.
We can iterate an array in 4 different modes:
- Front to end
- End to front
- Front to middle
- Middle to front
Let's take a look at each iteration mode with code sample.
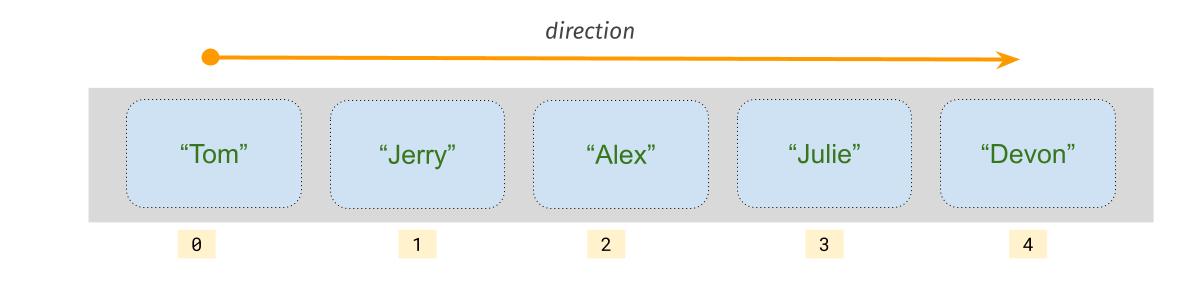
We visit each element of an array from first element to the last element.
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
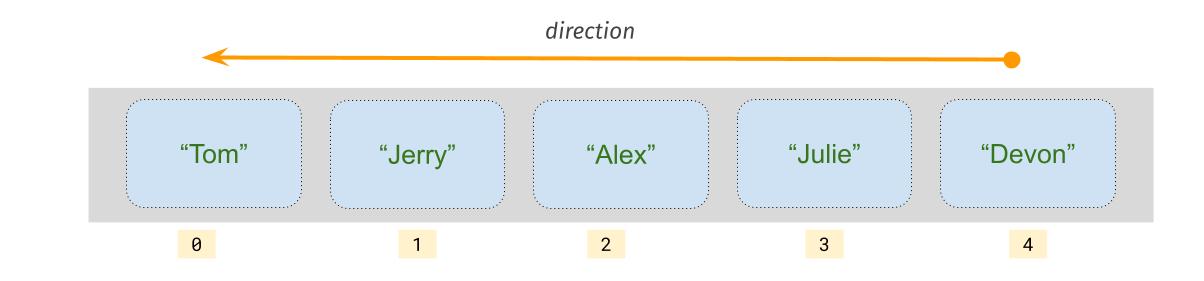
We visit each element of an array from last element to the first element.
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
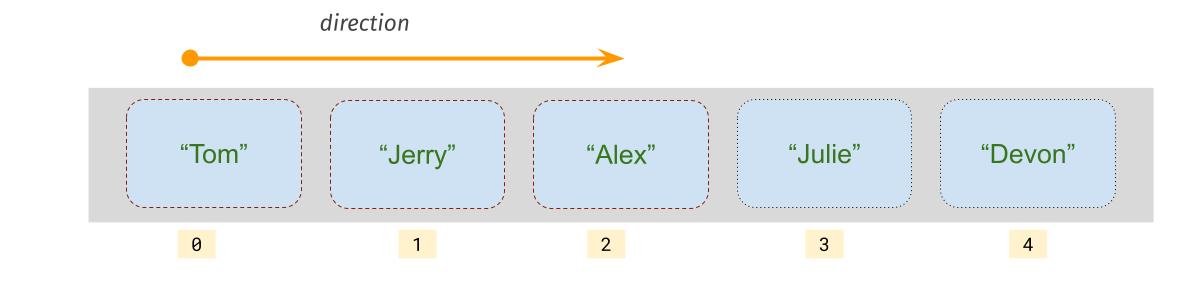
We visit half of array elements from first element to the middle element.
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
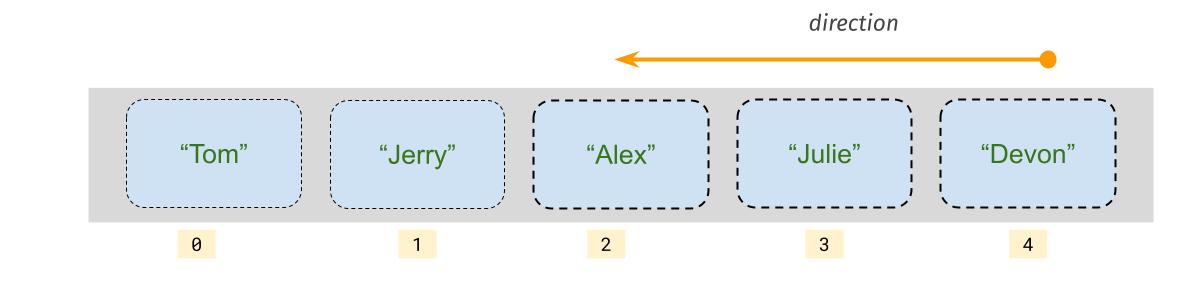
We visit half of array elements from last element to the middle element.
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
› Searching¶
We can search for specific element in the array using control statement like if statement.
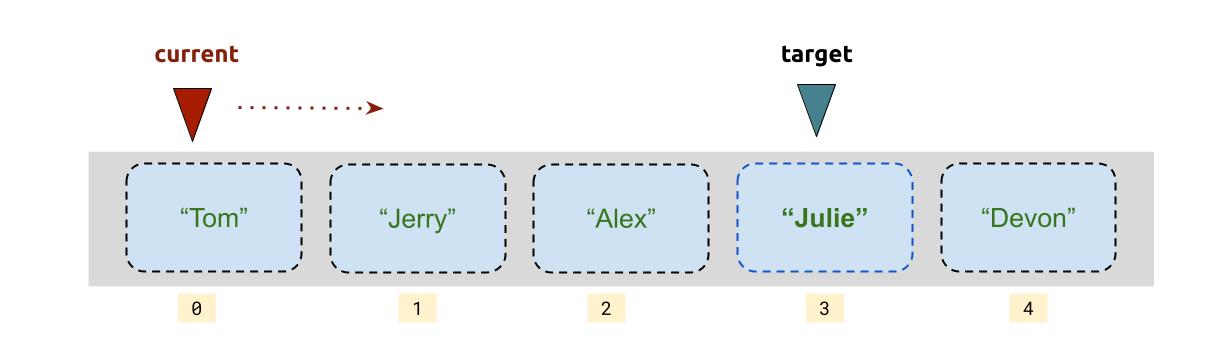
| finding target | |
|---|---|
| Output | |
|---|---|
One of the other prevalent array searching technique is finding a maximum number in the array. We will take care of this as follows:
- Start with first element as max
- Visit each array element and compare with max
- If current array element is bigger than max, then current element is the max
- If current array element is not bigger than max, move on to next element
| Finding max number in array | |
|---|---|
| Output | |
|---|---|
› Computation¶
Since array is collection of data, we can perform aggregated computation involving all the array elements. We will do this by using arithmetic operators.
We will take a look at following two examples:
- sum of all elements
- average of all elements
▩ Sum of all elements
In order to get sum of all the elements, we add each of the element as we visit them with simple array iteration.
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
| Output | |
|---|---|
▩ Average of all elements
As we get the sum of all elements, we can also get the average of elements by diving sum with array length.