Loops
In programming, loops are used to execute a specific code block repeatedly until a particular condition is met. Automation engineers use loops to perform similar test verifications over an over without having to write redundant test code.

Please watch following video for understanding general concept of loops:
Loop Explained
In this code note, we will cover following topics related to loops:
- for loop
- while loop
- do-while loop
- Infinite loop
- break and continue statement
› while Loop¶
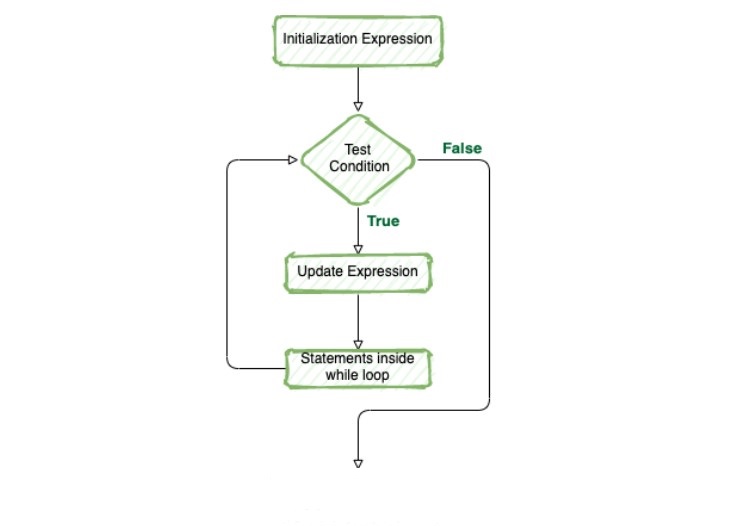
This loop is used to execute a block of code until condition result to boolean false value. If the number of code execution is not fixed, it is recommended to use the while loop.
In the above syntax, if the condition evaluates to true, then the following execution order will take place:
- statements inside the while loop body are executed, including the updater code.
- then, the test
conditionis evaluated again.
This process goes on until the condition is evaluated to false. When the expression is evaluated to false, the while loop is terminated. Note that code block may never execute as the expression can result in false from the start.
Flow Diagram
Note that the condition can be any of the following as long as it results in boolean data, which has two possible values true and false.
- boolean data value
- statement with relational operators
- statement with logical operators
- boolean expression
Try these sample codes in the editor:
Code Editor 👩💻
⚡For long lines of code, please click the
Edit this program in JDoodle.comlink
› do-while Loop¶
The do-while loop is similar to the while loop with one key difference. The body of the do-while loop is executed once before the condition is checked. Use this loop if the number of iterations is not fixed, and you must execute the loop body at least once before the start of loop execution.
| Syntax | |
|---|---|
The body of the do-while loop is executed once before checking the condition. After that, the condition is evaluated for the next loop iteration.
If the condition evaluates to true, code inside the loop body is executed once more, and the condition is re-evaluated. This process repeats until the condition evaluates to false.
Flow Diagram

Try this sample codes in the editor:
Code Editor 👩💻
⚡For long lines of code, please click the
Edit this program in JDoodle.comlink
› for Loop¶
The for loop is another variant of while loop, and it is by far the most used loop. Use this loop if the number of code block execution is fixed and you know exactly how many loop iteration you want to perform.
| Syntax | |
|---|---|
To summarize, the order of for loop executions :
- initialization always executes only once
- condition
- loop Body
- updater
- go back to step 2, terminate once it's
false, otherwise, do steps 2, 3, 4 again
Flow Diagram

Try the following sample code on code editor:
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
Code Editor 👩💻
⚡For long lines of code, please click the
Edit this program in JDoodle.comlink
› Infinite Loop¶
We should always be careful while working with loops. The loop will run forever if we mistakenly set the condition to be never false. This situation is called an infinite loop. Let's look at how we can make an infinite loop with each loop type.
while loop example
do-while loop example
for loop example
› break and continue¶
Depending on the circumstances, it is sometimes desirable to terminate or skip the loop iteration. In Java, we can terminate the loop execution using the break statement and skip the current loop body iteration using the continue statement. You should understand that these two statements are only usable with if statement inside the loop body.
break statement:
The break statement terminates the loop immediately if its encountered, and execution resumes to the next statement following outside the loop.
example flow
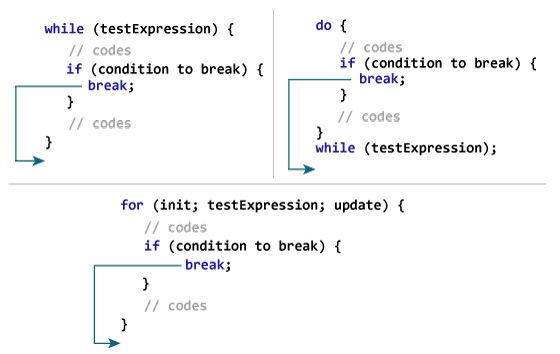
| Sample Code | |
|---|---|
continue statement:
The continue statement skips the current iteration of a loop and the control of the program moves to the execution of next loop iteration.
example flow
