Operators
The primary purpose of a program is to manipulate stored data. Out of the package, Java offers operators for basic data manipulation capabilities for primitive data types.

In this module, we will cover the following topics:
- What are Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Compound Assignment Operators
- Logical Operators
- Relational Operators
- Ternary Operator
› What are Operators¶
Operators are special symbols that carry out operations ( manipulations ) on data values. It allows us to manipulate data stored in variables and use its result.
| Code Sample | |
|---|---|
Because of the addition operator at line 6, we were able to get new data(30) from two existing data ( 10 and 20 ).
Here is the full list of operators we will cover in this note:
| Operators | Symbol | What it does |
|---|---|---|
| Assignment Operator | = |
assigns data to a variable |
| Arithmetic Operator | +, -, /, *, % |
basic math calculations |
| Compound Assignment Operator | +=, -=, /=, *=, %= |
updates the content of a variable |
| Unary Operators | ++, -- |
updates the content of a variable by 1 |
| Relational Operators | >, <, >=, <=, ==, != |
compares two numbers |
| Logical Operators | &&,ll, ! |
manipulates boolean data |
| logical assignment operator | (condition)? |
assigns the data value based on a condition |
Note that the operators we will touch base work on the following primitive data types:
- int
- double
- char
- boolean
› Assignment Operator¶
Symbol: =
Assignment operators are used for assigning data values to variables. The assignment operator gives the data value on its right to the variable on its left.
assignment operator

Note right side of the assignment operator can be any of the following as long as it results in a single data value and data value and the variable data type must match.
- data value
- a non-empty variable
- a method call that returns a data value
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
› Arithmetic Operator¶
Arithmetic operators are used for performing basic mathematical calculations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
| Symbols | What it does |
|---|---|
+ |
Addition |
- |
Subtraction |
* |
Multiplication |
/ |
Division |
% |
Modulus, Gets remainder |
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
Modulus Operator
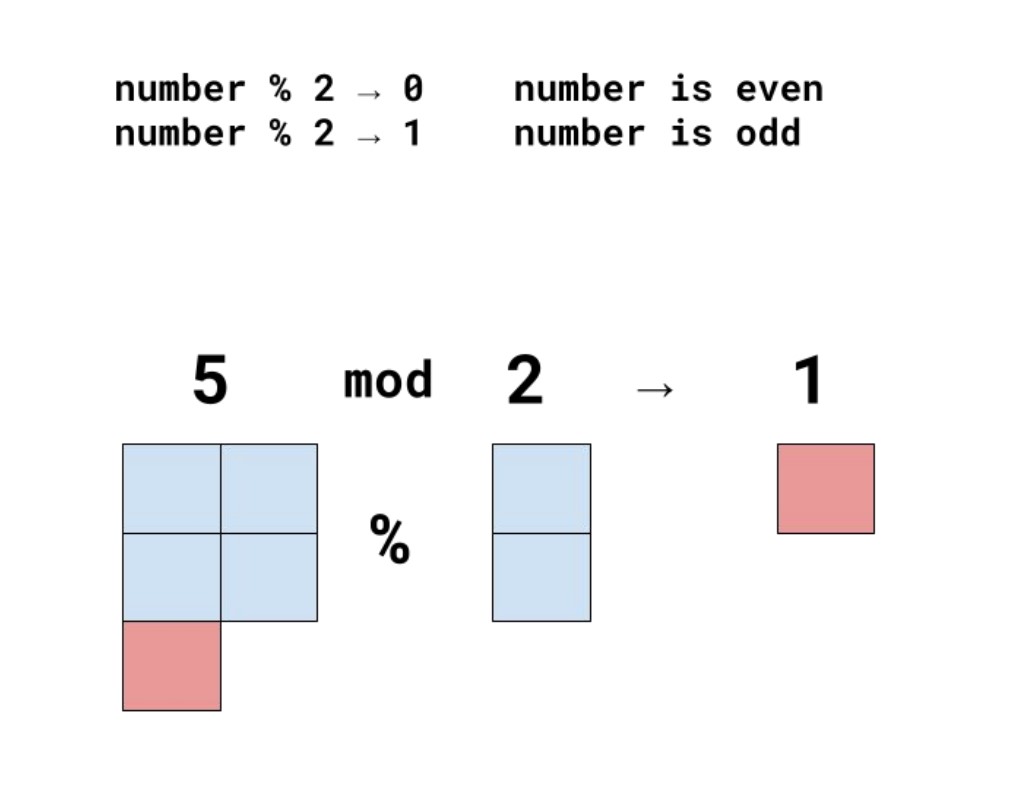
The modulus operator (% ) is especially useful to do simple things like figuring out if a given number is even or odd and more complex tasks like detecting a cycle.
If you mod any integer number with 2, you will get either 0 or 1 as an answer, if the answer is:
- 0 : the number is Even number
- 1 : the number is Odd number
› Unary Operators¶
Also known as Increment & Decrement operator. It is used for updating the numerical variable's content by one. The update operation is either added by one or subtracted by one.
| Symbols | What it does |
|---|---|
++ |
Update the numerical variable content by adding 1 |
-- |
Update the numerical variable content by subtracting 1 |
It has two different modes of usage known as prefix mode and postfix mode:
The content of the integer variable will be first displayed to the console, and afterward, its content will be incremented by 1.
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
› Content Updater¶
Also known as a compound assignment operator, it simplifies the syntax of variable content updating code. We can use this for primitive data types and reference data types like String.
For numerical data types such as int, double, char:
| Symbols | What it does | Example | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|---|
+= |
update by addition | x+=5 | x = x + 5 |
-= |
update by subtraction | x-=5 | x = x - 5 |
*= |
update by multiplication | x*=5 | x = x * 5 |
/= |
update by division | x/=5 | x = x / 5 |
%= |
update by modulus | x%=5 | x = x % 5 |
For text data types such as String:
| Symbols | What it does | Example | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|---|
+= |
update by concatenation | s+="hello" | s = s + "hello" |
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
› Relational Operators¶
It is used for comparing two numerical data types. The result of this operator is a boolean data value, true or false, depending on comparisons.
| Symbols | Description | Example ( same results fordouble,char) |
|---|---|---|
== |
equal to | 5 == 3 🠚 false4 == 4 🠚 true |
!= |
not equal to | 5 != 3 🠚 true4 != 4 🠚 false |
> |
greater than | 5 > 3 🠚 true4 > 4 🠚 false 4 > 24 🠚 false |
>= |
greater than or equal to | 5 >= 3 🠚 true4 >= 4 🠚 true 4 >= 24 🠚 false |
< |
less than | 5 < 3 🠚 false4 < 4 🠚 false 4 < 24 🠚 true |
<= |
less than or equal to | 5 <= 3 🠚 false4 <= 4 🠚 true 4 <= 24 🠚 true |
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
› Logical Operators¶
Used for processing logical expressions, which is the basis for decision-making in the program. Works on two boolean data values and produces another boolean data value as a result.
Syntax:
| Operator Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
ll |
true if either of the boolean value is true |
false ll true 🠚 true |
&& |
true if all of the boolean value is true |
false && true 🠚 false |
! |
inverts the value of a boolean value | !true 🠚 false |
Please try this code sample on your test case method:
› Ternary Operator¶
Also called conditional assignment operator, it is used for assigning data based on comparison.
symbol: ( )? :
The conditional operator or ternary operator is shorthand for the if-then-else statement. Its syntax is as follows.
- If the
conditionistrue, thenexpression1is assigned to thevariable. - If the
conditionisfalse, thenexpression2is assigned to thevariable.
| Code Sample | |
|---|---|