User Inputs
When we trigger our test automation execution on dedicated servers, we will initiate test process by providing test related input and config details in Terminal. It's vital for us to be able to process user inputs.

In this code note, we will cover following topics:
- What is User Inputs
- Scanner Class
- String Concatenation
- Summary
› What is User Inputs¶
In terminal based application, end user can interact with the application through text inputs. The term User Inputs refers to these text inputs provided by the end user as part of using the terminal application.
As an example, the terminal based echo program lets you provide text inputs for printing out echo message.
Providing input to echo application
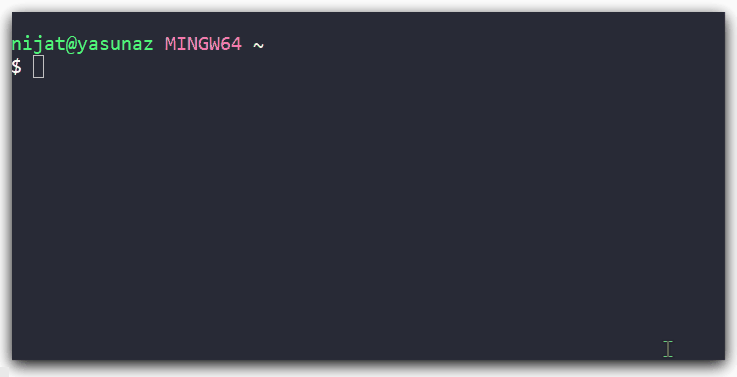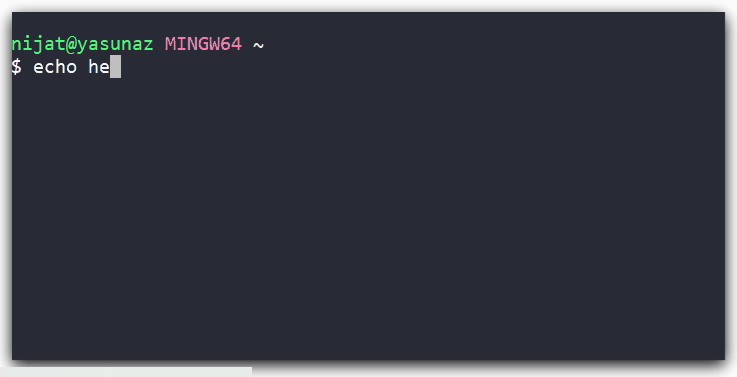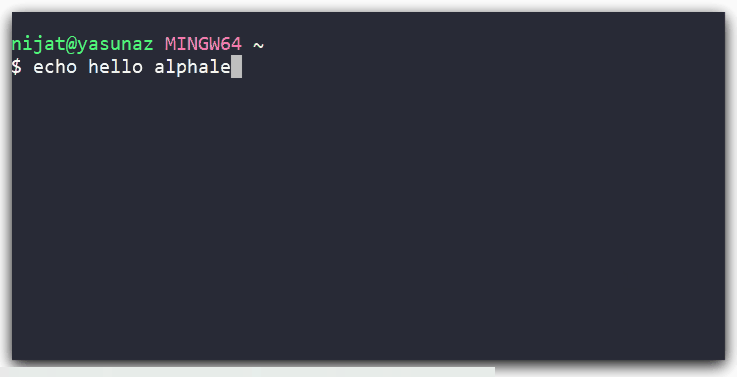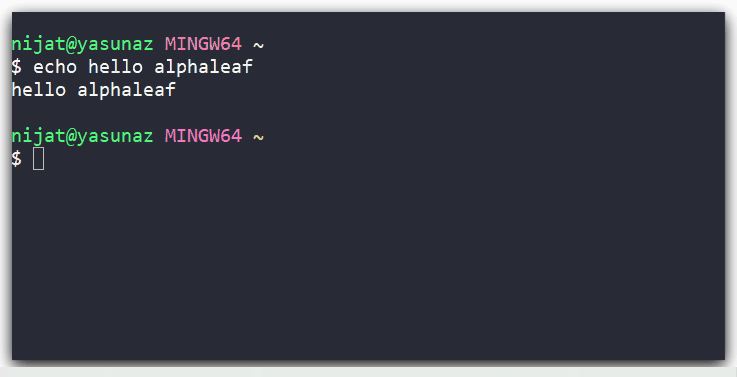
From above sample:
echo: it is the program namehello alphaleaf: it is the user inputs provided by the end uesr
Note that everything you type in the terminal window is treated as text data (String).
› Scanner Class¶
In Java, user input for terminal based Java application is supported by methods grouped in theScanner class. We can use these methods in this class by creating a code copy ( called Class Object ) of this class.
This class contains useful methods that enable use to parse the user inputs from the terminal window.
You can process any user inputs by following three easy steps.
Step 1: Create a Scanner object:
Step 2: Prompt & Process the inputs:
Step 3: Destroy the Scanner object:
Some useful methods includes:
| Method Name | Method usage purpose |
|---|---|
scan.next() |
Used for parsing one complete word input |
scan.nextLine() |
Used for parsing single line of text inputs |
scan.nextInt() |
Used for parsing single integer number input |
scan.nextDouble() |
Used for parsing single decimal number input |
scan.nextBoolean() |
Used for parsing single logic data input |
› String Concatenation¶
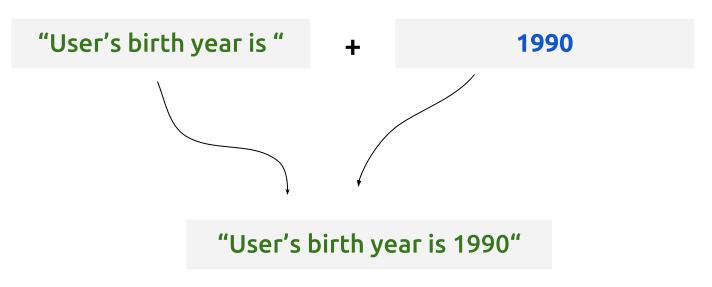
String data uses concatenation operator for combining two different string data into one larger string data. This operator is especially useful when you are forming output string.
- operator symbol:
+
Note that string concatenation operator converts all the non-string data type operand into String data type as long as one side of the operator is string data.
| Right Side is Number | |
|---|---|
| Left Side is Number | |
|---|---|