Data Type
Essentially, a program is a collection of instructions on manipulating and storing data. For a program to work with data, it must recognize the data. This code note will cover how Java allows us to represent data we use on daily basis.

We will cover following topics:
- What is Data Type
- Primitive Data Type
- Reference Data Type
› What is Data Types¶
It is a representation of data we use daily in Java programs. It specifies the size and types of data values supported in your code. Before you can express and work with any data in Java, it must be designed and enabled in the language.
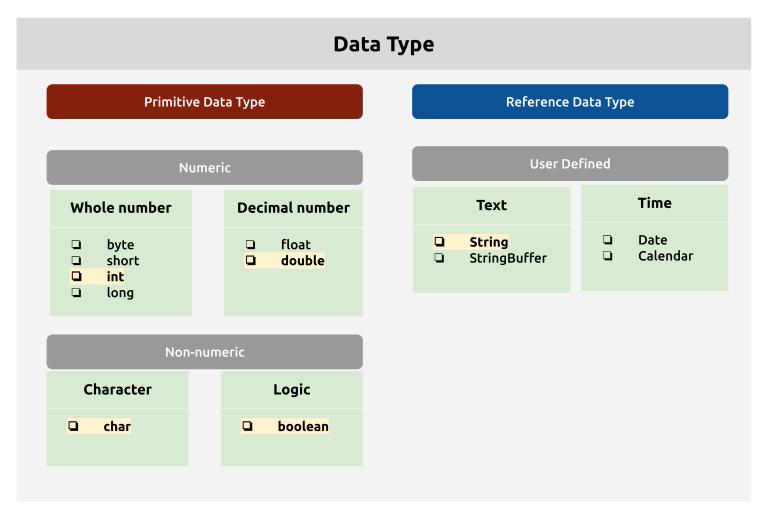
Data types in Java comes in two forms:
- Primitive Data Type : data types that comes with Java language
- Reference Data Type : custom data type created by developers
Java Data Type Map
Once the data type is specified in the Java language, when you use these in your code, the computer system knows how to interpret them.
When you type a number, character, or String in your Java program. Java can detect and treat them as data values.
› Primitive Data Type¶
Created by Java language engineers, Java users will be able to represent fundamental data, such as numbers, characters, and logical data. The primitive data type is built into the Java language itself.
List of Primitive Data Type:
| Data Type Symbol | Represents | Example Data Value | Data Value Range |
|---|---|---|---|
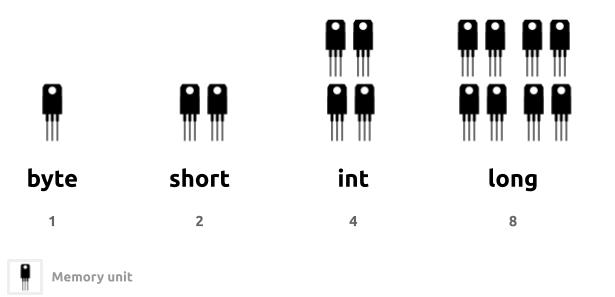
byte |
Whole numbers | -19, 0, 19 | 217 to +128 |
short |
Whole numbers | -19, 0, 19 | -32768 to +32767 |
int |
Whole numbers | -19, 0, 19 | -2 Billion to +2 billion |
long |
Whole numbers | -19L, 0L, 19L | -9 QT to +9QT |
float |
Decimal numbers | -19.03F, 0.0F, 19.84F | n/a |
double |
Decimal numbers | -19.07, 0.001, 19.76 | n/a |
char |
Single character | 'A', 'a', '?', '#' | n/a |
boolean |
Single logical data | true, false | 2 data values only |
Please note that byte, short, int, and long data types represent the same whole numbers. The only difference between them is the storage capacity. It requires more storage in the computer to represent and hold a number 1900990 than it does for 78.
› Reference Data Type¶
Java language does not support data types such as Time, Pictures, and Music out of the package. Instead, the programmer must create data representations they will need in their program. This custom-made data type is known as Reference Datatype.
One example of a Reference Data Type is a String data type, which was custom-made to represent text in Java. It was created by a developer who wanted to represent text and paragraphs in a Java program.
| Data Type Symbol | Represents | Example Data Value |
|---|---|---|
String |
Text data such as paragraph and phrases. | "Hello, Alphaleaf students! how are you?" |
We will learn how to create custome Data Type of our own when we cover Object Oriented Programming.