Console Output
The test automation framework we will create is a terminal-based test execution program. Its test execution output displays in the terminal for quick test progress feedback. Therefore, being able to print text to the terminal (console) window is essential.

In this module, we will cover the following topics:
- Code Commenting
- print() Method
- Escape Characters
- println() Method
› Code Commenting¶
Before we get into coding, let's review the importance of code commenting. Code commenting is the practice of sprinkling short, normally single-line notes throughout your code. These notes are called comments.
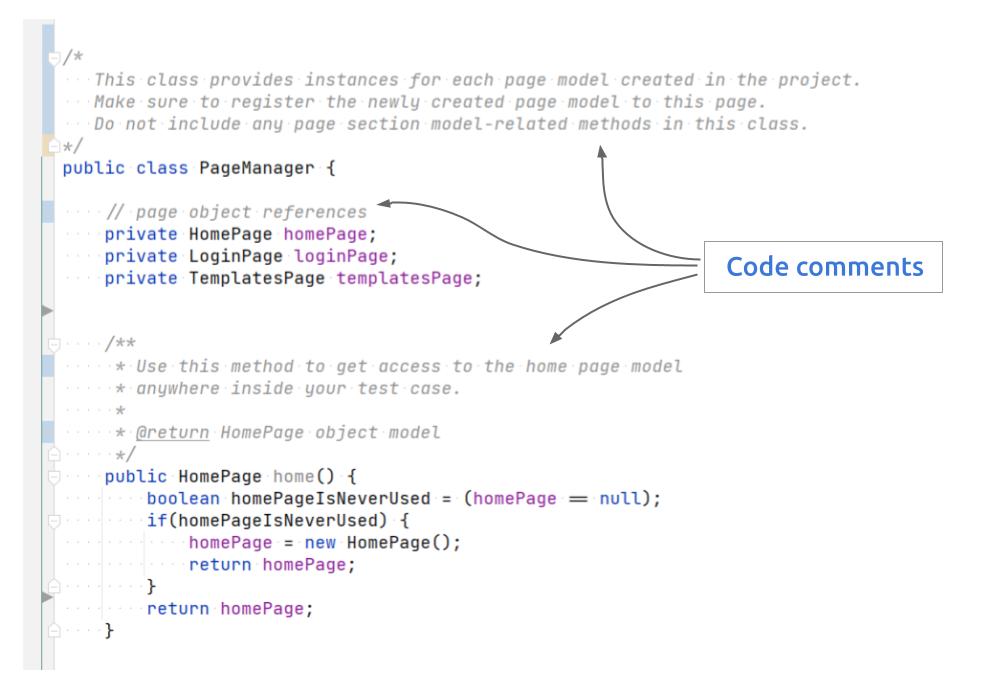
They explain how your program works and your intentions behind it. Comments don't affect your program since it's not a code, but they are invaluable for people reading your code.
There are three types of Java comments:
- Single-line comments
- Multi-line comments
- Documentation comments
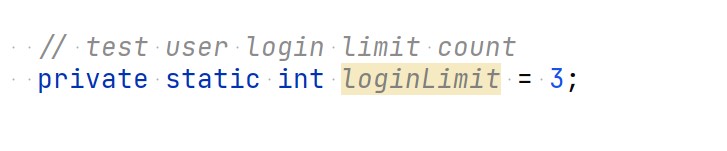
Used for explaining single line of code. The comments starts with // symbol.
Used for explaining multiple lines of code or methods, block of code with multiple lines. This comment starts with /* and ends with */.

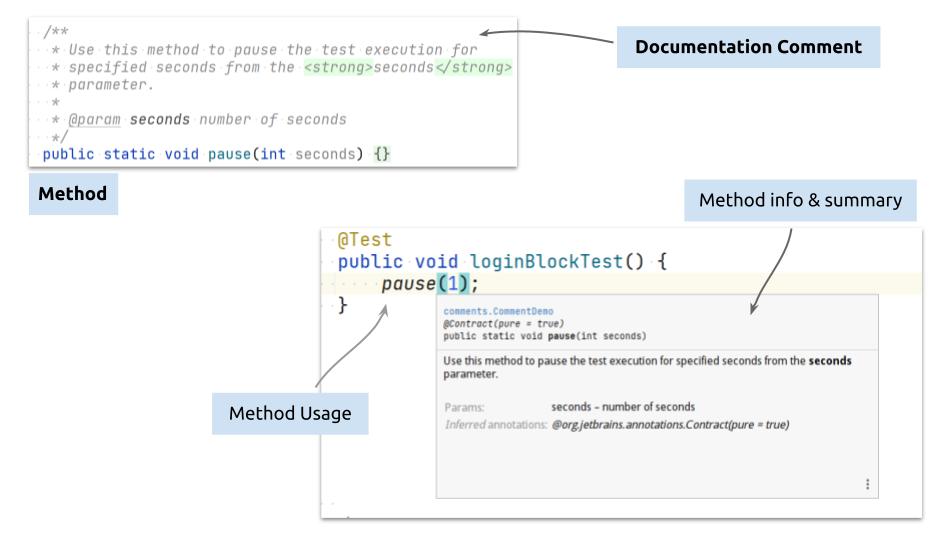
Used for commenting method that you created for the other programmers, who is going to use your method in the project. This comment tarts with /** and ends with */
› print() method¶
The print() command tells the CPU to display a text to the terminal while the cursor remains at the end of the displayed text.
print command
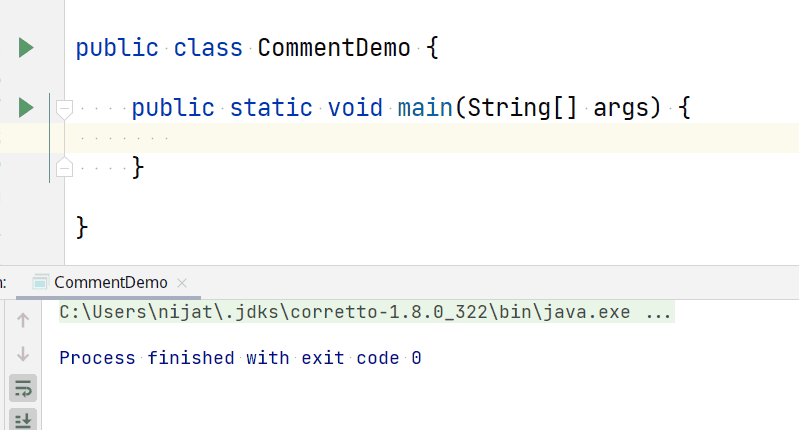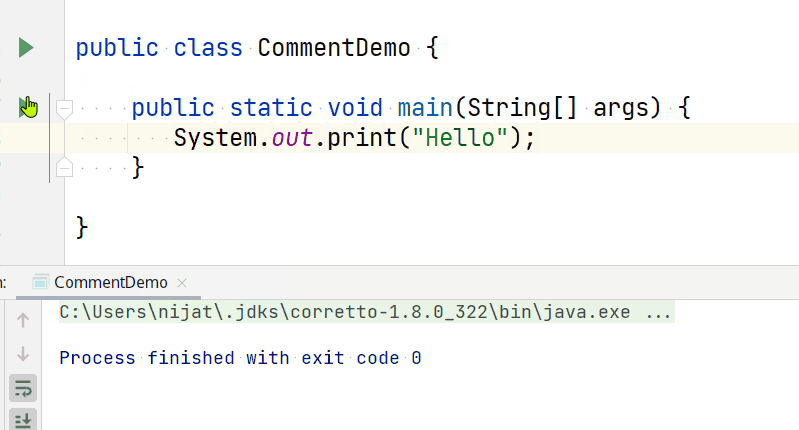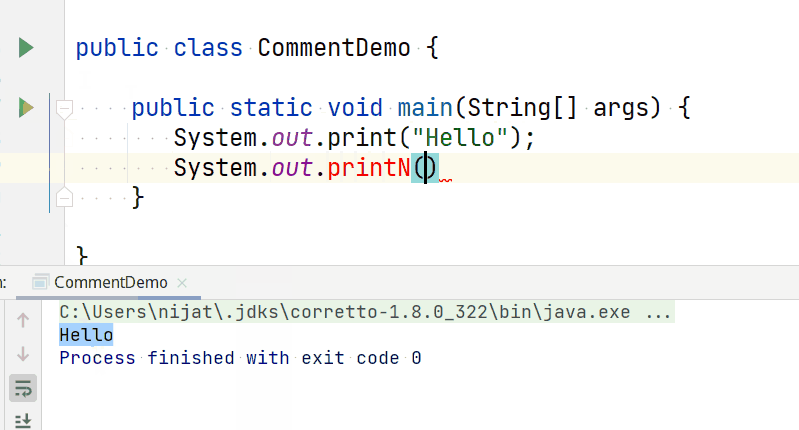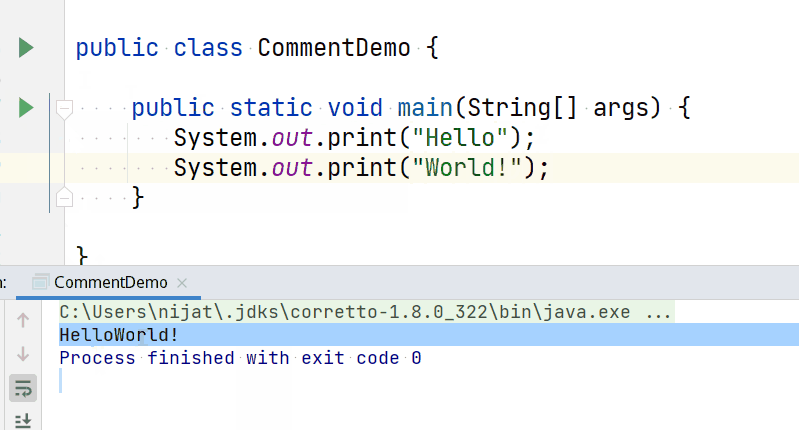
So if you have a code like the below:
You will get an output like this:
To instruct the CPU to print text to the next text output line, you have to use \n escape character that represents a new line in the console, and subsequent terminal output will start from the next line.
print command with \n
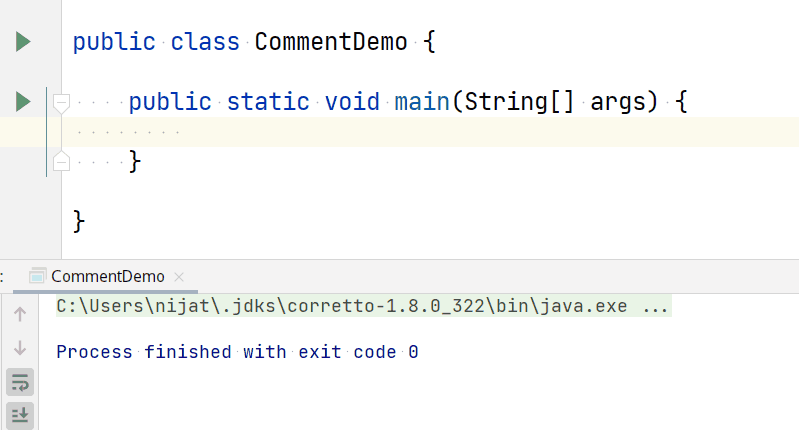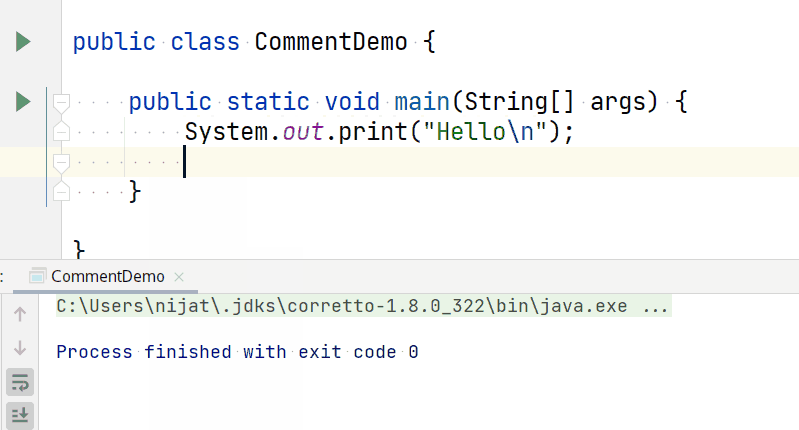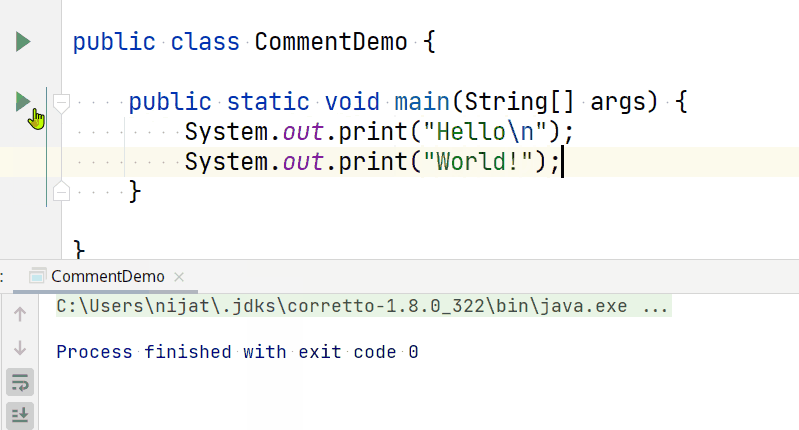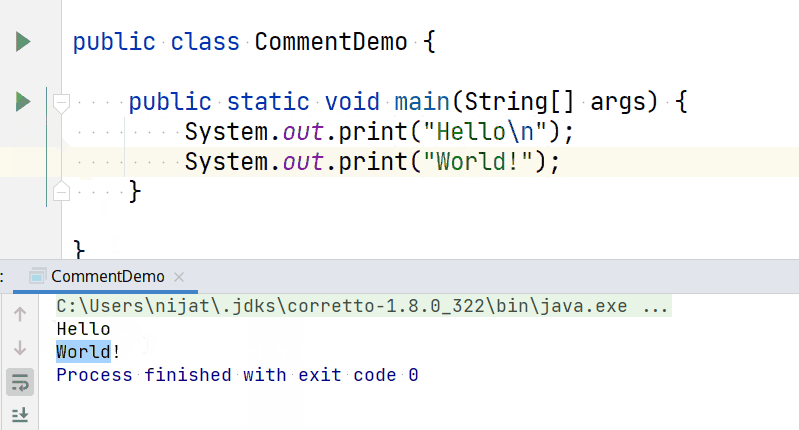
So writing a code like below:
Will produce output like this:
› Escape Characters¶
Also called escape sequence, we can use special characters to change the console's text output behavior. In Java, escape characters begins with \ to distinguish them from regular characters.
The list of escape sequences we use:
| Character | Console output behavior |
|---|---|
\n |
Moves cursor to the next line |
\' |
Displays single quotations |
\" |
Displays double quotations |
\t |
Inserts 4 space characters |
\r |
Moves back the cursor to the front of the line |
\b |
Inserts a backspace one character |
Please watch the following video to better understand escape character usage:
Escape Characters explained
Code template in the video:
› println() method¶
The println() command tells the CPU to display a text to the terminal and insert a new line at the end. This command is a combination of print() method with \n escape character.
println command
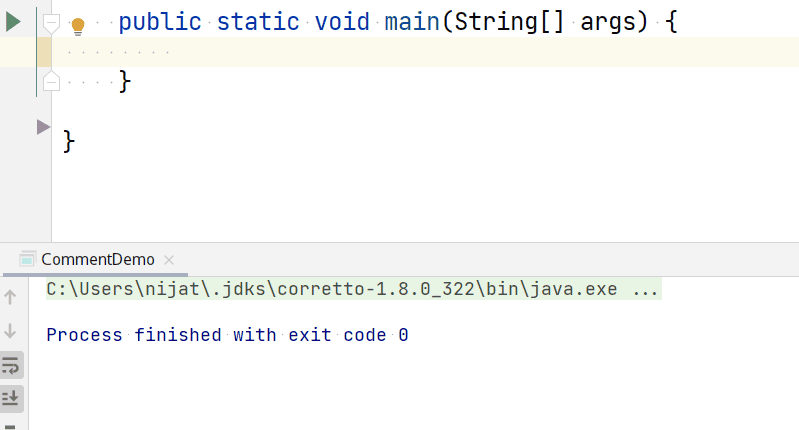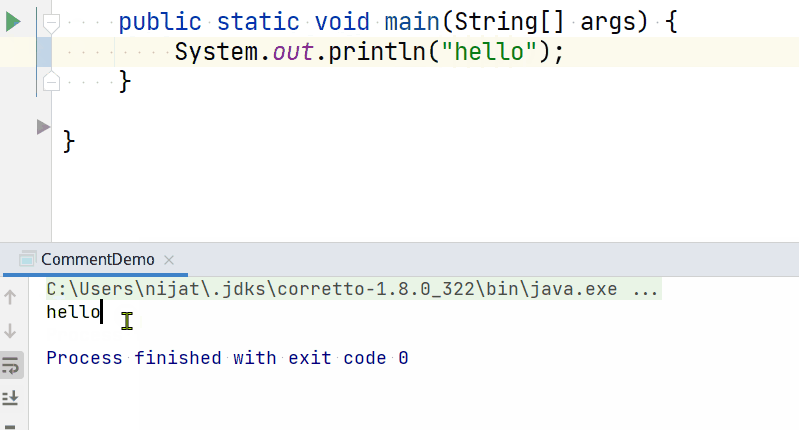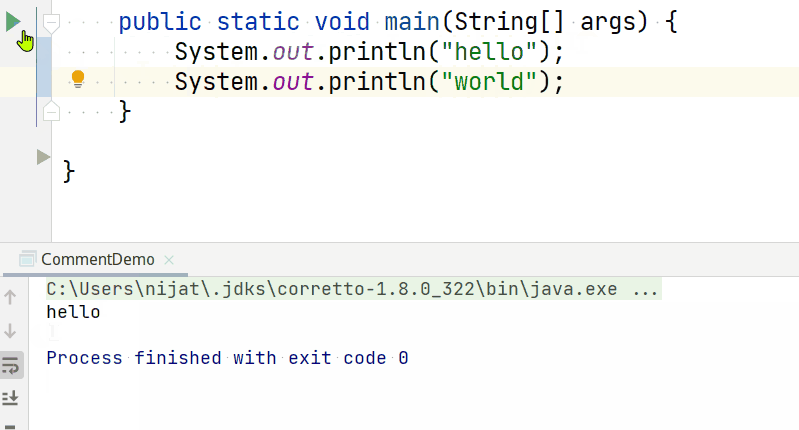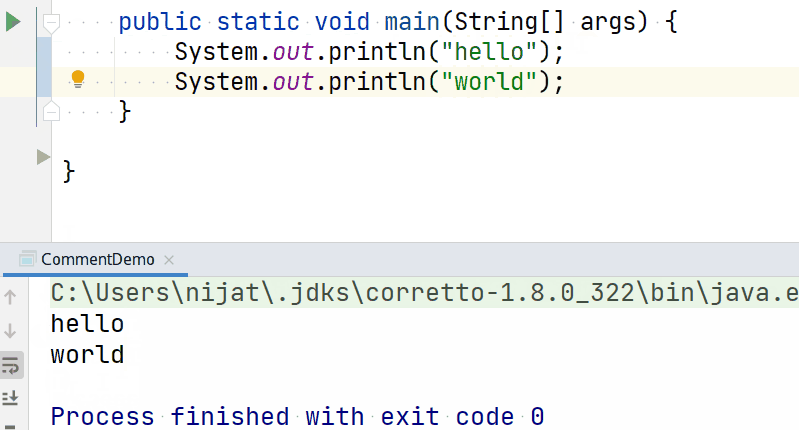
So if you have a code like below:
Will produce text output with an empty new line:
As you can see the comparison between the print() method with println() method, the following code is identical: